Cell Division
When some of your cells die, new ones are created; but what exactly is this process called and how does it happen ?
Well there are two types of cell reproduction; they are mitosis and meiosis.
Well there are two types of cell reproduction; they are mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis
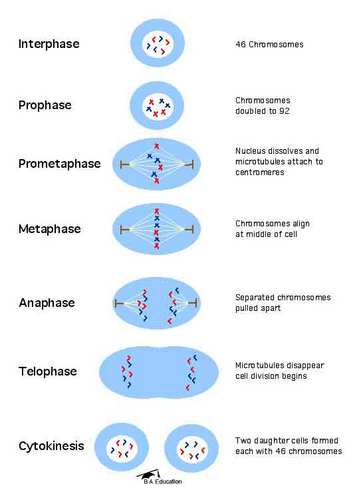
The process of mitosis. Source: http://www.ba-education.com
Mitosis is the process of cell reproduction where the two daughter cells produced are identical to the parent cells. This process can happen in single cell organisms such as bacteria and some plants (through their cuttings). Mitosis also occurs in almost every cell of the human body except the red blood cells, nervous tissue and the gametes (sperm and ova).
The purpose of mitosis is so single cell organisms can reproduce and to produce new cells for the human body to grow and develop. It is also for producing new cells to replace damaged and dead cells such as skin cells as well as repairing organ tissue.
The DNA doubles its chromosomes into two sets of chromosomes and then splits in half to create two new daughter cells.
The purpose of mitosis is so single cell organisms can reproduce and to produce new cells for the human body to grow and develop. It is also for producing new cells to replace damaged and dead cells such as skin cells as well as repairing organ tissue.
The DNA doubles its chromosomes into two sets of chromosomes and then splits in half to create two new daughter cells.
Meiosis
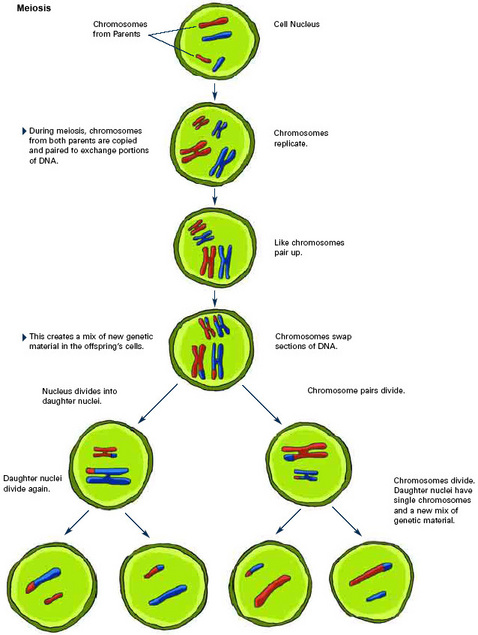
Process of Meiosis. Source: http://schoolworkhelper.net/wp-content/uploads/2010/11/meiosis.jpg
Meiosis is the process of cell division that is only necessary in sexual reproduction. It is to reproduce a new organism consisting of two cells, one from the mother and one from the father.
The process occurs when the diploid cells (homologous chromosomes) duplicates its two sets of chromosomes (one from mother, one from father) and splits into four haploid cells. In each haploid cell produced, there are 23 chromosomes.
Each of the resulting chromosomes in the cells contains a combination of DNA from their parents. This means that the resulting offspring will have a blend of characteristics from both its mother and father but still making it distinct from them.
In the resulting daughter cells, they each contain one cell from each of their parents. If the cells inside are XX, then the resulting offspring will be a female. If they are XY, then the offspring will be a male. Males are more prone to sex linked diseases such as colour blindness. This is because the disease is usually located on the X chromosome and since males only have one X chromosome they have a higher chance of getting the disease. Whereas on females they have two X chromosomes, so they only get the disease if both of the X chromosomes have the disease (depending on if the disease is dominant or recessive; in this case, colour blindness is recessive).
The process occurs when the diploid cells (homologous chromosomes) duplicates its two sets of chromosomes (one from mother, one from father) and splits into four haploid cells. In each haploid cell produced, there are 23 chromosomes.
Each of the resulting chromosomes in the cells contains a combination of DNA from their parents. This means that the resulting offspring will have a blend of characteristics from both its mother and father but still making it distinct from them.
In the resulting daughter cells, they each contain one cell from each of their parents. If the cells inside are XX, then the resulting offspring will be a female. If they are XY, then the offspring will be a male. Males are more prone to sex linked diseases such as colour blindness. This is because the disease is usually located on the X chromosome and since males only have one X chromosome they have a higher chance of getting the disease. Whereas on females they have two X chromosomes, so they only get the disease if both of the X chromosomes have the disease (depending on if the disease is dominant or recessive; in this case, colour blindness is recessive).
