DNA
Source: http://www.dna-sequencing-service.com
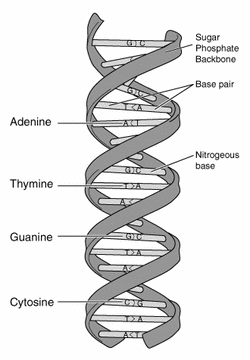
DNA, which is also known as deoxyribonucleic acid, is the fundamental building block needed to make all the structures in the body that are needed to function. These DNA contain the characteristics of what make you who you really are and different to everyone else. Most DNA can be found in the cell nucleus however a small amount can be found in the mitochondria. The molecule of DNA is quite large, thus it is tightly stranded into what is known as a double helix. It is a winding, two-stranded chemical structure which looks quite similar to a twisted ladder.
DNA is made up of building blocks called nucleotides. Nucleotides are linked into chains with alternating sugar groups and phosphate backbones with one of four nitrogen bases. There are four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides, they are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). These bases bond in pairs; A with T, C with G. The sequence of these bases make up your genetic code which determines your biological structure such as the colour of your hair.
DNA is made up of building blocks called nucleotides. Nucleotides are linked into chains with alternating sugar groups and phosphate backbones with one of four nitrogen bases. There are four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides, they are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). These bases bond in pairs; A with T, C with G. The sequence of these bases make up your genetic code which determines your biological structure such as the colour of your hair.
Genes
Source: http://www.dnassequencing.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/Genes.jpg
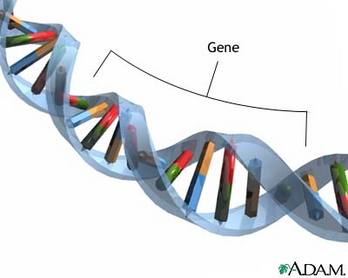
One section of DNA that contains the instruction to make up a protein is called a gene. These genes can vary in size depending what they are coding for; with many that could contain up to 1 million bases in just one gene!
Proteins are coded by the genes. Proteins are made up of many different amino acids (there are about 20 different amino acids located in the body). The number and order of amino acids in the protein determines the function of the protein (whether it is an enzyme or a muscle fibre). A string of 3 bases (triplet) is the code for one amino acid. The number and order of triplets determines the order and number of amino acids, and therefore, the protein formed.
Genes are also used to code for when the protein begins and stops. But also for how active the protein is; you don't want too much hair to grow at once! It also codes for when the protein is active.
Proteins are coded by the genes. Proteins are made up of many different amino acids (there are about 20 different amino acids located in the body). The number and order of amino acids in the protein determines the function of the protein (whether it is an enzyme or a muscle fibre). A string of 3 bases (triplet) is the code for one amino acid. The number and order of triplets determines the order and number of amino acids, and therefore, the protein formed.
Genes are also used to code for when the protein begins and stops. But also for how active the protein is; you don't want too much hair to grow at once! It also codes for when the protein is active.
Chromosomes
Source: http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/illustrations/chromosomes.jpg
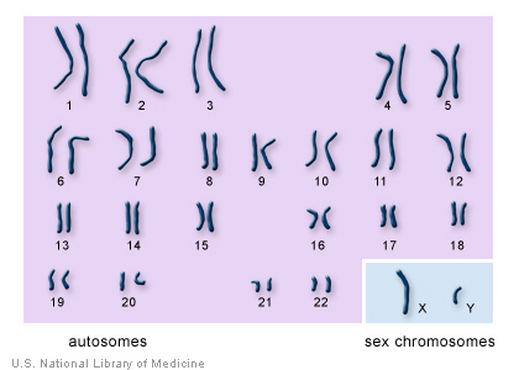
Of course, because each cell is very small and they need to fit many molecules into just one cell, each DNA molecule is tightly packed into what is known as a chromosome. DNA spends most of its time in chromosome form however during cell division, the DNA unwinds itself so it can be copied and transferred to new cells.
Most cells in the human body contain 46 chromosomes, in 23 homologous pairs. However in the sperm and egg cells there exists 46 chromosomes in 22 pairs plus an X and Y chromosome (male) or an X and X chromosome (female). These complete set of chromosomes are also known as diploid cells.
Most cells in the human body contain 46 chromosomes, in 23 homologous pairs. However in the sperm and egg cells there exists 46 chromosomes in 22 pairs plus an X and Y chromosome (male) or an X and X chromosome (female). These complete set of chromosomes are also known as diploid cells.
